Diagnostic And Therapeutic ECRP Procedure For Bite Duct Store And Malignant Biliary
Home > Services
Endoscopic Variceal Ligation
What is ERCP?
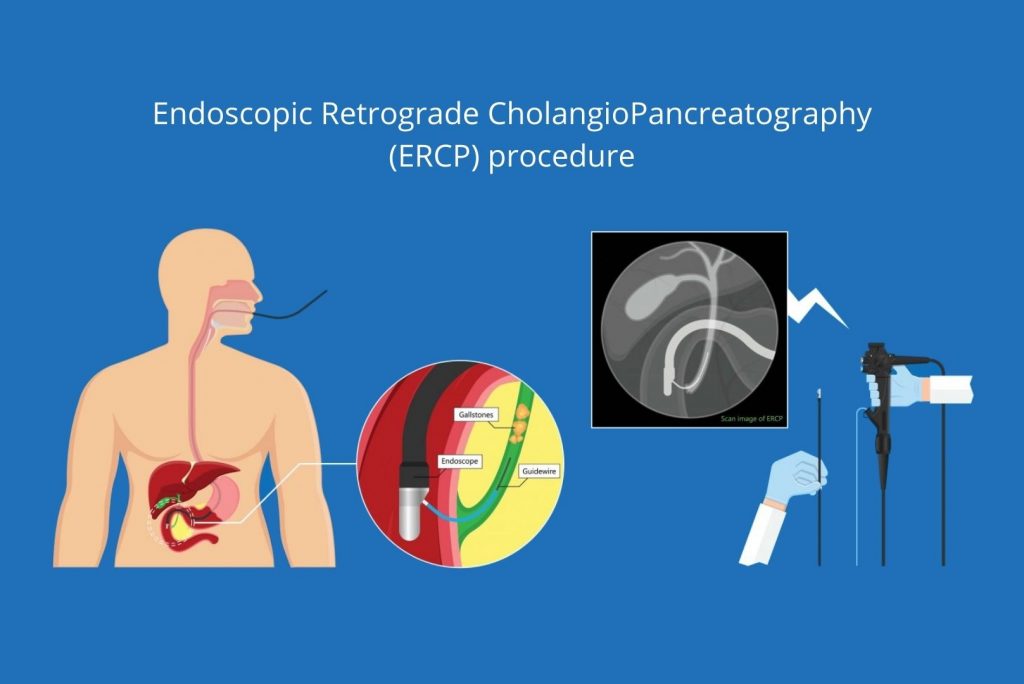
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a procedure that combines upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and x-rays to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
Bile ducts are tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and duodenum. Pancreatic ducts are tubes that carry pancreatic juice from the pancreas to the duodenum. Common bile duct and main pancreatic duct join before emptying into the duodenum.
Why is ERCP performed?
ERCP is used to diagnose and treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
ERCP is performed when bile or pancreatic ducts have become narrowed or blocked because of the following conditions:
- Gallstones that form in the gallbladder and become stuck in common bile duct
- Infection
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Trauma or surgical complications in bile or pancreatic ducts
- Pancreatic pseudocysts
- Tumours or cancers of the bile ducts
- Tumours or cancers of the pancreas
What are the pre-requesters?
To see the upper GI tract clearly, the fasting of at least 8 hours is required.
How do doctors perform ERCP?
Doctors who have specialized training in ERCP perform this procedure. An intravenous needle will be placed in your arm to provide a sedative. Sedatives help you stay relaxed and comfortable during the procedure. A healthcare professional will give you a liquid anaesthetic to gargle or will spray anaesthetic on the back of your throat. The anaesthetic numbs your throat and helps prevent gagging during the procedure. The healthcare staff will monitor your vital signs and keep you as comfortable as possible.
After ERCP, you may be asked to stay in the hospital for a few hours till the sedation wears off. During this period, you will be supervised by health care professionals. ERCP is generally safe when carried in expert hands.